2. 链表
203. 移除链表元素
- 203. 移除链表元素
- 0505,easy,answer
设置一个虚拟头指针,用来解决如果 head 结点要删除时,需要移动 head 的特殊情况。
var removeElements = function (head, val) {
// 虚拟头节点
const res = new ListNode(0, head);
let cur = res;
while(cur.next) {
if (cur.next.val === val) cur.next = cur.next.next;
else cur = cur.next;
}
return res.next; // 返回虚拟头节点指向的下一个指针。
};
707. 设计链表
- 707. 设计链表
- 0505,mid,answer
- 链表的定义,链表的处理
错误:找了很久的错误:
// ❗️拼写错误要注意
this._tail // 写成了 this.tail
this._head // 写成了 this_head
// 要注意边界问题,每一个函数在开始是,都要考虑到现处理边界情况。
需要先自定义三个方法(对象):
- 定义公共方法:
// 创建一个单链表的结点
class LinkNode {
constructor(val, next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next || null;
}
}
// 链表存储:长度、头指针、尾指针
var MyLinkedList = function () {
this._size = 0;
this._head = null;
this._tail = null;
};
// 根据 index 获取链表中的某个节点
MyLinkedList.prototype.getNode = function (index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this._size) return null;
// 如果要最后一个,可以快速定位一下,省去 for 循环
if (index === this._size - 1) return this._tail;
let cur = this._head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
答案 (需要加上上面的三个方法):
// 根据 index 获取链表中的某个节点
MyLinkedList.prototype.getNode = function (index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this._size) return null;
// 如果要最后一个,可以快速定位一下,省去 for 循环
if (index === this._size - 1) return this._tail;
let cur = this._head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
/**
* @param {number} index
* @return {number}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.get = function (index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this._size) return -1;
// 获取节点值
return this.getNode(index).val;
};
/**
* @param {number} val
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtHead = function (val) {
const node = new LinkNode(val, this._head);
this._size += 1;
this._head = node;
// 如果链表中还没结点
if (this._size === 1) this._tail = node;
};
/**
* @param {number} val
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtTail = function (val) {
const node = new LinkNode(val, null);
this._size += 1;
// 如果链表中还没结点
if (this._size === 1) {
this._head = node;
this._tail = node;
return
}
this._tail.next = node;
this._tail = node;
};
/**
* @param {number} index
* @param {number} val
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtIndex = function (index, val) {
if (index > this._size) return;
// 头插入
if (index <= 0) this.addAtHead(val);
// 尾插入
else if (index === this._size) this.addAtTail(val);
// 正常插入
else {
const pre = this.getNode(index - 1); // 找到要插入的index的前一个结点
pre.next = new LinkNode(val, pre.next);
this._size += 1;
}
};
/**
* @param {number} index
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.deleteAtIndex = function (index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this._size) return;
// 处理头节点
if (index === 0) {
this._head = this._head.next;
this._size -= 1;
// 如果链表中没有结点了,额外处理尾结点
if (this._size === 0) this._tail = null;
return;
}
// 按照 index 查找前一个结点
const pre = this.getNode(index - 1);
pre.next = pre.next.next;
// 处理尾结点
if (index === this._size - 1) this._tail = pre;
this._size -= 1;
};
206. 反转链表
- 206. 反转链表
- 0505,easy,quick
方法一:双指针
- pre 指向前一个结点,cur 指向当前要修改的结点,temp 作为临时结点,指向 cur.next。
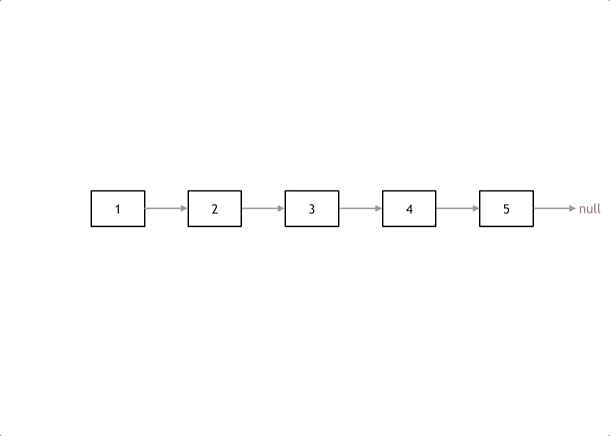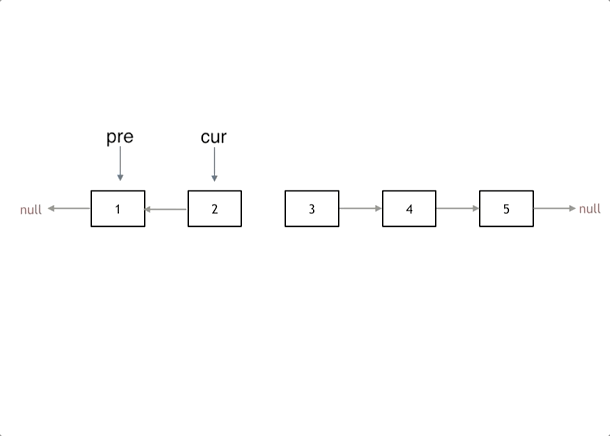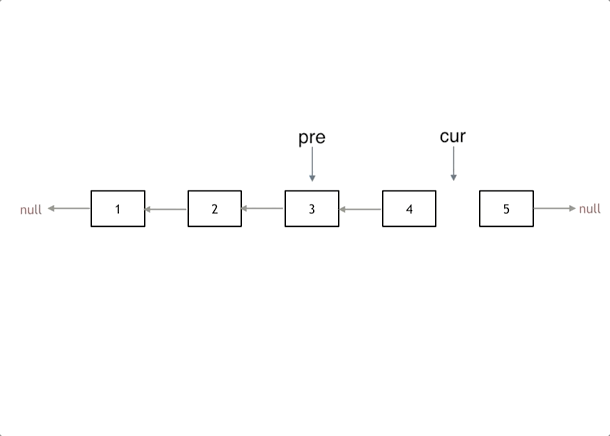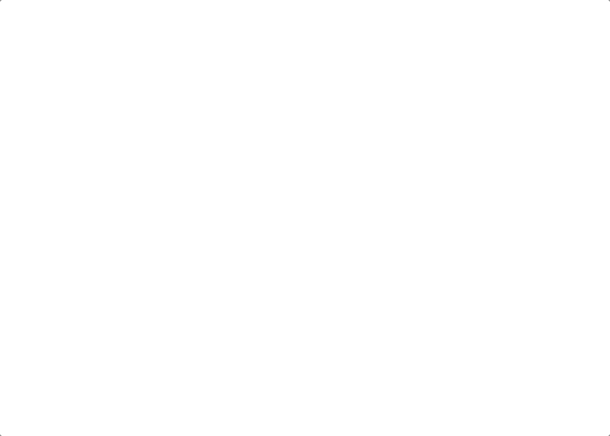
var reverseList = function (head) {
let [pre, cur] = [null, head];
while (cur) {
const temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
// pre�、cur 往前移动
[pre, cur] = [cur, temp];
}
return pre;
};
方法二:迭代
逻辑和双指针是一样的。
var reverseList = function (head) {
return reverse(null, head);
function reverse(pre, cur) {
// 结束递归
if (!cur) return pre;
const temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
};
方法三:栈
如果要求不原地修改,而是重新构建一个 nodeList 则使用栈结构来复制:
var reverseList = function (head) {
const stack = [];
const resList = new ListNode();
// 原链表的 val 全部入栈:
for (let cur = head; cur !== null; cur = cur.next) {
stack.push(cur.val);
}
// 将栈中的 val 写入新链表中:
for (let cur = resList; stack.length; cur = cur.next) {
cur.next = new ListNode(stack.pop());
}
return resList.next;
};
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 0505,mid,quick
方法一:三指针
交换链表,需要改动 3 处结点的 .next 关系,也就是说需要三个指针。
-
需要定义一个虚拟头指针,以解决 head 结点也需要移动的问题;
-
可以自己画个图,就明白逻辑了。
-
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)。
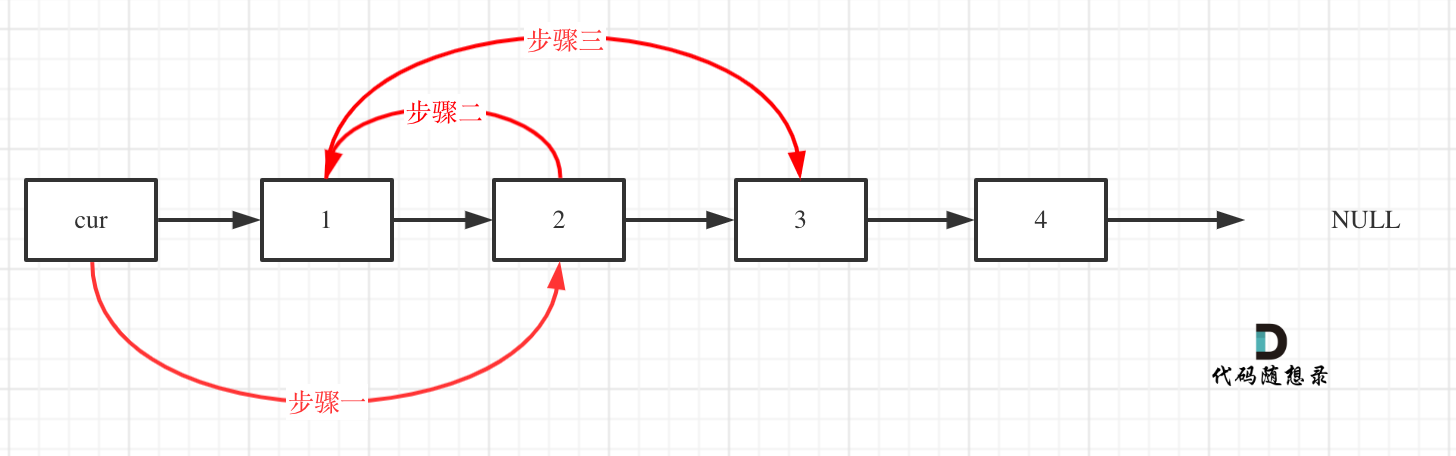
一共有�三步,但顺序可以反过来:
var swapPairs = function (head) {
if (!head || !head.next) return head;
// 虚拟头节点
const res = new ListNode('', head);
// cur 指向两个被交换节点前的一个结点
// 交换两个结点:change 和 change.next (也就是temp).
let [cur, change] = [res, head];
while (change && change.next) {
const temp = change.next;
change.next = temp.next; // 步骤三
temp.next = change; // 步骤二
cur.next = temp; // 步骤一
// 指针往前移动
cur = change;
change = change.next;
}
return res.next;
};
方法二:迭代
// 返回,head 和 head.next 完成交换的链表
var swapPairs = function (head) {
if (!head || !head.next) return head;
// newNode 是后面交换好的链表
const newNode = swapPairs(head.next.next);
// head 和 head.next(temp) 交换位置,交换后链表头就是tamp了,所以return temp。
const temp = head.next;
temp.next = head;
head.next = newNode;
return temp;
};
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 0505,mid,quick
双指针 / 快慢指针:
- left 和 right。right 在 left 的右边,与 left 一直保持 n 的距离。
- right 从 index = n 开始向后遍历,直到遍历到链表的结尾为止,
- 此时 right 则指向了待删除节点的前一个结点,也就是说
left.next结点即将被删除;
- 此时 right 则指向了待删除节点的前一个结点,也就是说
- ⚠️ 栈结构也可以,先把所有节点放入栈中,然后向外取 n 个节点,则正好取出带删除节点的前一个节点。
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
res = new ListNode('', head); // 虚拟头
let [left, right] = [res, res];
// right 指针先走 n 个距离
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) right = right.next;
// left 和 right 一起走,直到 right 指向链表尾
while (right.next) {
[left, right] = [left.next, right.next];
}
// 此时 left 指向带删除节点的前一个结点
left.next = left.next.next;
return res.next;
};
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
- 面试题 02.07. 链表相交
- 0505,easy,answer
- 双指针
错误原因:
- 这里涉及到当变量有点多:有两个链表、两个指针、两个长度。所以需要对每一个操作步骤仔细核对。我就是在其中有很多小错误:
- 变量没有定义直接使用;
- while 循环时,只移动了变量 a,没有移动变量 b;
- 已经定义了一个变量 curL,再后面把 curL 改名时,没有对所有的 curL 全部更换名字。
方法一:双指针|求长度
求两个链表交点节点的指针。 交点不是数值相等,而是指针相等。所以在一个链表上,可能存在多个相同值的节点。
- 先求出两个链表各自的 长度,并求出两个链表长度的 差值
gap。 - 代码中, curA 永远指向更长的一个链表,此时让 curA 移动到,和 curB 末尾对齐的位置,也就是向后移动
gap个距离。 - 然后就可以用 while 循环,同时遍历 curA 和 curB 了,当他们两个相等时,则表明指向了同一个节点,返回即可。
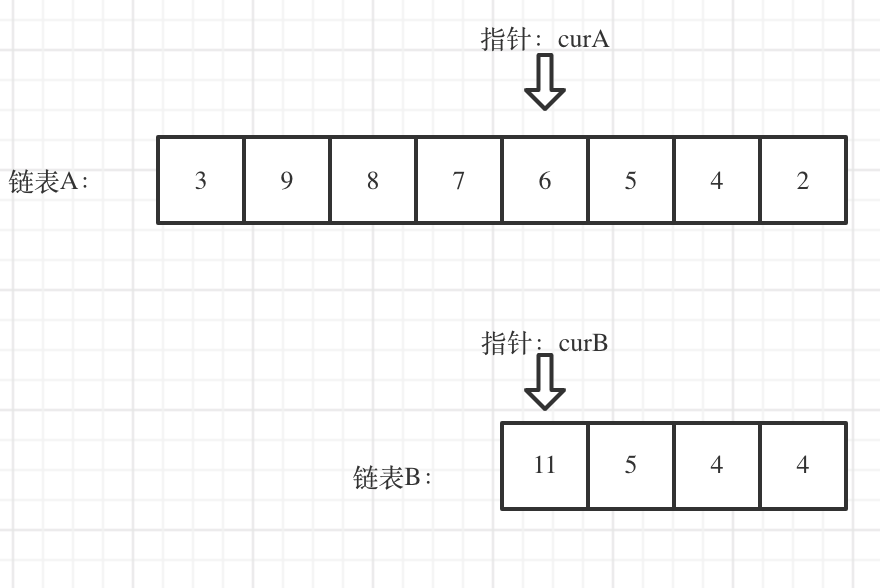
时间复杂度:两次获得链表的长度:O(m+n),然后从头遍历一次链表:O(m) ==> O(m + 2n) 假设 n 为 更短的一边
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
// 拿到更短的一个, lenA is longer
let [lenA, lenB] = [getLen(headA), getLen(headB)];
if (lenA < lenB) {
[lenA, lenB] = [lenB, lenA];
[headA, headB] = [headB, headA];
}
let gap = lenA - lenB;
// 对长链表进行移动
let [curA, curB] = [headA, headB];
while (gap-- > 0) curA = curA.next;
while (curA) {
if (curA === curB) return curA;
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
// 获取链表的长度:时间复杂度 O(n)
function getLen(list) {
let len = 0, cur = list;
while (cur) {
cur = cur.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
};
方法二:双指针|数学思维
- 总结数学规律:🔗.

- 时间复杂度:O(a+b) 空间复杂度:O(1)。 节点指针 A , B 使用常数大小的额外空间。
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
if (headA === null || headB === null) {
return null;
}
let pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA !== pB) {
pA = pA === null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB === null ? headA : pB.next;
console.log(pA, pB);
}
return pA;
};
方法三:Set|哈希集合
-
利用
Set只能保存 唯一value,且 有序 来确定是否指向同一节点。 -
流程:
- ��把
headA中所有节点放入 set 中(O(n)); - 把从头遍历
headB,直到发现 cur 和 set 已经保存的某个指针指向同一个节点,证明从这个节点开始后面都是重复的。O(m) - 返回找到的节点。
- ��把
-
时间复杂度:O(m+n),其中 m 和 n 是分别是链表 head 和 headB 的长度。需要遍历两个链表各一次。
空间复杂度:O(m),其中 m 是链表 headA 的长度。需要使用哈希集合存储链表 headA 中的全部节点。
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
const set = new Set();
let cur = headA;
while (cur !== null) {
cur.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = headB;
while (cur !== null) {
if (cur.has(cur)) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
};
142. 环形链表 II
- 142. 环形链表 II
- 0506,mid,quick
方法一:Set|哈希集合
和上题(面试题 02.07.)的方法三一样,使用 set 哈希集合来解决找多指针指向同一节点的问题。
- Set 具有两个特点:成员仅有 value 且唯一;成员有序且按照加入时间排序。
var detectCycle = function (head) {
const set = new Set();
let cur = head;
while (cur) {
if (set.has(cur)) return cur;
set.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return null
};
方法二:快慢指针
具体可以看这里。
简单说,就是 fast 一次两步,slow 一次一步。
- 判断是否有环(图一):如果 fast 和 slow 相遇,就是有环;
- 判断环的入口(图二):从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点 也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点。
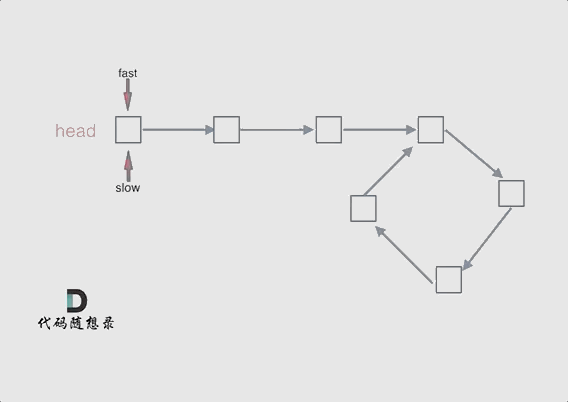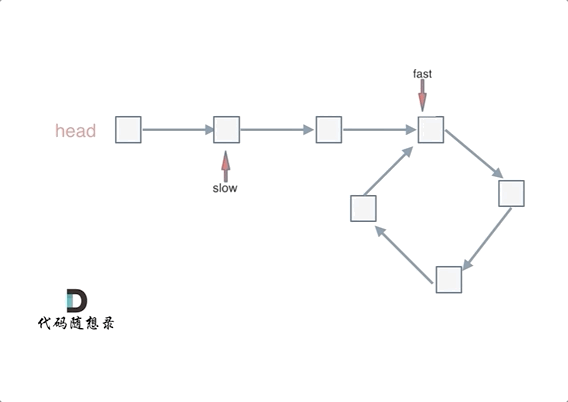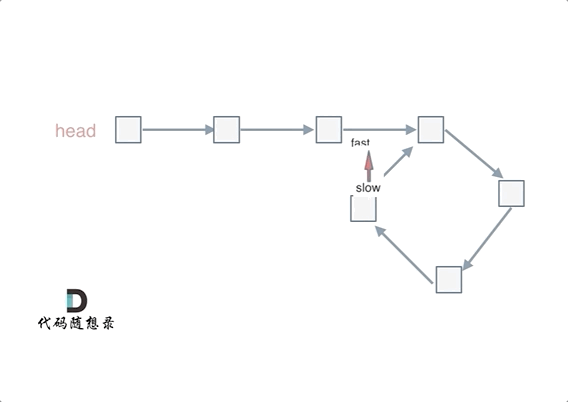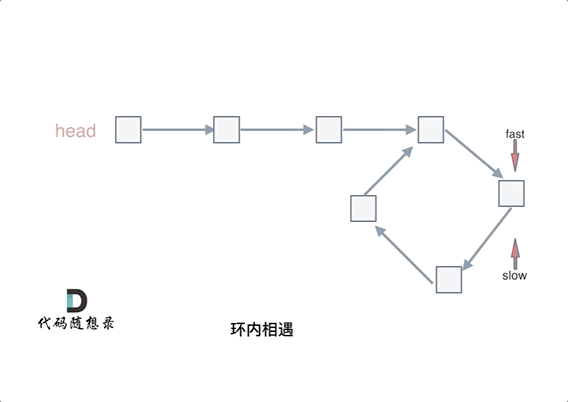
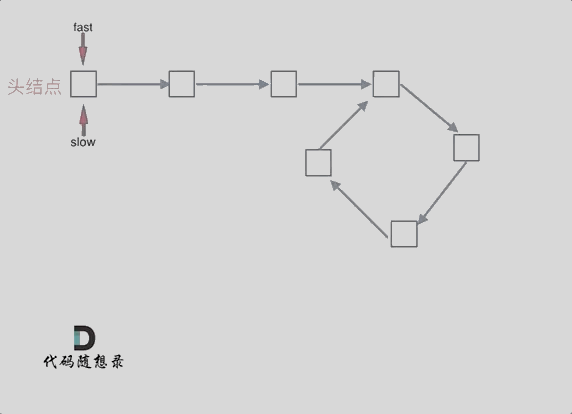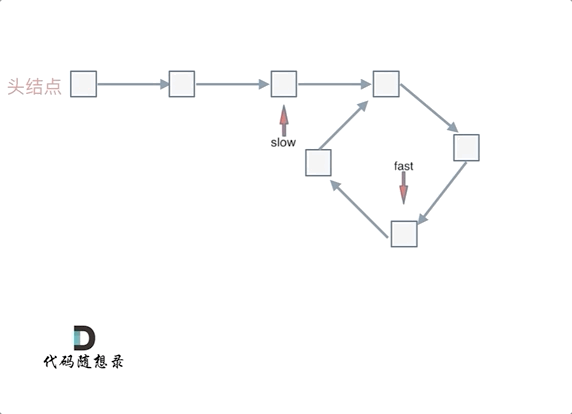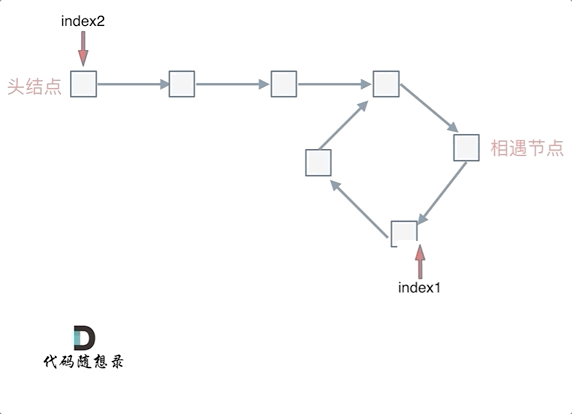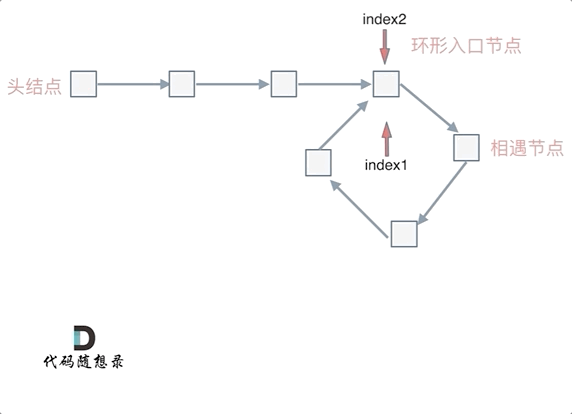
var detectCycle = function (head) {
if (!head || !head.next || !head.next.next) return null;
// 判断环形
let [slow, fast] = [head.next, head.next.next]; // ❗️注意,这里先走一步,不能 [head, head.next] 这样不算完整的一步
while (slow !== fast) {
if (!fast.next || !fast.next.next) return null; // 遍历到链尾,当前环形不存在
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 判断入口 slow 从头走, fast 从交点往后走
slow = head;
while (slow !== fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
};
======= experience =============================================
链表、带有 index 操作的题:
- 在 iPad 上简单的绘制流程图,和 code,可以使调理更清晰。
======= summary 1 =============================================
Map 和 Set 的区别:
- Set 和 Array 类似,没有 key,只有 value。与 array 不同的是,Set 的 key 是唯一的。
- Map 和 Object 类似,有 key 和 value。与 Object 不同的是,Map 的 key 不仅仅是 string、symbol,还可以是任何类型。
关于 Set、Map 的操作 API 和 迭代方式:
记录几个特殊的:
- 迭代通常用
for ... of,Map 和 Set 使用方法相同。for (const key of myMap.keys()、for (const value of myMap.values()、for (const [key, value] of myMap.entries())、
- 增加一个成员有不同:
Map.set()、Set.add();
问:js 里面 Map 和 Set 存 / 取的时间复杂度?
Map 和 Set 仅仅作为 JS 中的��类型出现,并没有所谓的规范源码,其实现完全取决于各家浏览器的 JS 引擎怎么做。
-
虽然浏览器的实现没有约束,但是哈希表可以实现O(1)存取时间复杂度,浏览器没理由实现得更差吧。
-
以 Chrome 的 V8 引擎为例,其有关
Map的源码在 https://github.com/v8/v8/blob... 中,感兴趣可以自己去阅读。主要运用的是 Hash Table,时间复杂度是 O(1)。 -
综上,可以认为 map 和 set 的存取时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
我们遇到了要快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里的时候,就要考虑哈希法。
Set 就是一个 hash table。
- 代码随想录:哈希表。
2. 两数相加
- 2. 两数相加
- 0613,mid,answer
- 链表基础
为什么没做出来?
p1、p2 两个指针分别指向两个待相加的链表,当较短的已经遍历完,还需要遍历较长的链表时,
- 我的处理方案:把较长的链表后续节点直接接到结果 p3 上,然后判断是否需要进位。如果要进位,则再向后遍历每个节点,改变节点的值。
- 更好的处理方案:不会把较长链表的后续节点直接接在结果链表中,而是令较短链表的值当作 0,当作两个链表都有值,正常的相加和进位。当两个链表都遍历完,判断是否还有进位,有的话创建最后一个节点赋值为 1
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) {
// 是否进位
let nextVal = 0;
const root = new ListNode(0, null);
let p1 = l1, p2 = l2, p3 = root;
while (p1 || p2) {
// console.log(p1.val, p2.val, nextVal);
// 如果有其中一个为空,则跳过添加该位
const p1Val = p1 ? p1.val : 0;
const p2Val = p2 ? p2.val : 0;
const sum = p1Val + p2Val + nextVal;
nextVal = sum >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
p3.next = new ListNode(sum % 10); // 创建当前节点并添加值
// 重置指针
p1 = p1?.next;
p2 = p2?.next;
p3 = p3.next;
}
// 此时l1,l2两个节点都为空,判断如果有进位,则创建最后一个节点赋值为1;
if (nextVal) p3.next = new ListNode(1);
return root.next;
};
21. 合并两个有序链表
- 21. 合并两个有序链表
- 0619,easy,quick
- 链表基础
方法一:迭代
要点:
- head 需要创建一个空白链表头,剩下的节点就不需要 new nodeList 创建新链表了,只需要
cur = p1 / p2赋值整个链表节点。
var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) {
if (!list1) return list2;
const head = new ListNode();
let cur = head;
let p1 = list1;
let p2 = list2;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1.val < p2.val) {
cur.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
cur.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 有一个到头了
if (!p1 || !p2) cur.next = !p1 ? p2 : p1;
return head.next;
};
方法二:递归
- 定义递归函数返回值
mergeTwoLists 函数的返回值,就是一个已经合并好的有序链表。
- 定义递归截止
当 list1 和 list2 有一个链表达到了末尾,则直接返回另一个链表的剩余节点即可。
- 定义递归逻辑
函数永远返回的链表头节点一定是对小的:
- 如果 list1 更小,则当前 mergeTwoLists 返回 list1 节点。
- 在返回之前,给
list1.next后续链表节点排序合并,递归调用mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);即可。
var mergeTwoLists = function (l1, l2) {
// 有一个节点为空
if (!l1) return l2;
if (!l2) return l1;
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
};